A silent heart attack, also known as a silent myocardial infarction (SMI), is a heart attack that occurs without any noticeable symptoms. It’s called “silent” because the person experiencing it may not even realize they’ve had a heart attack. This type of heart attack is more common than you might think, and it’s important to understand the symptoms and risk factors associated with it.
What is a Silent Heart Attack?
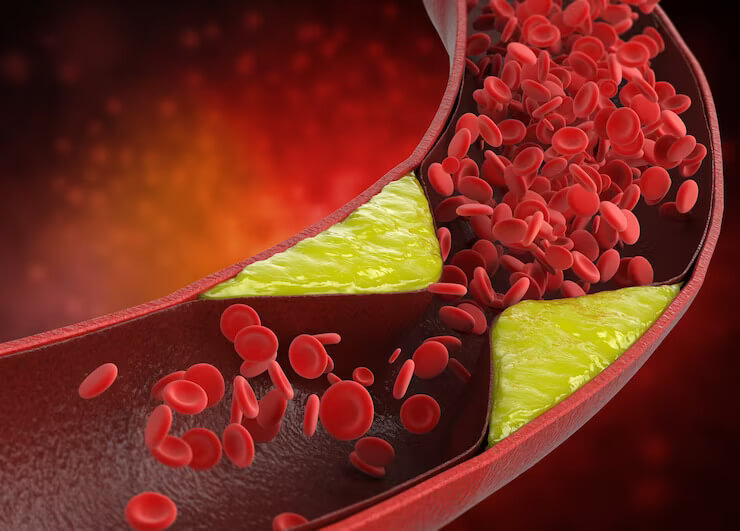
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can damage the heart muscle, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications or even death. In a silent heart attack, the blockage occurs in a similar way, but there are no obvious symptoms.
Symptoms of a Silent Heart Attack
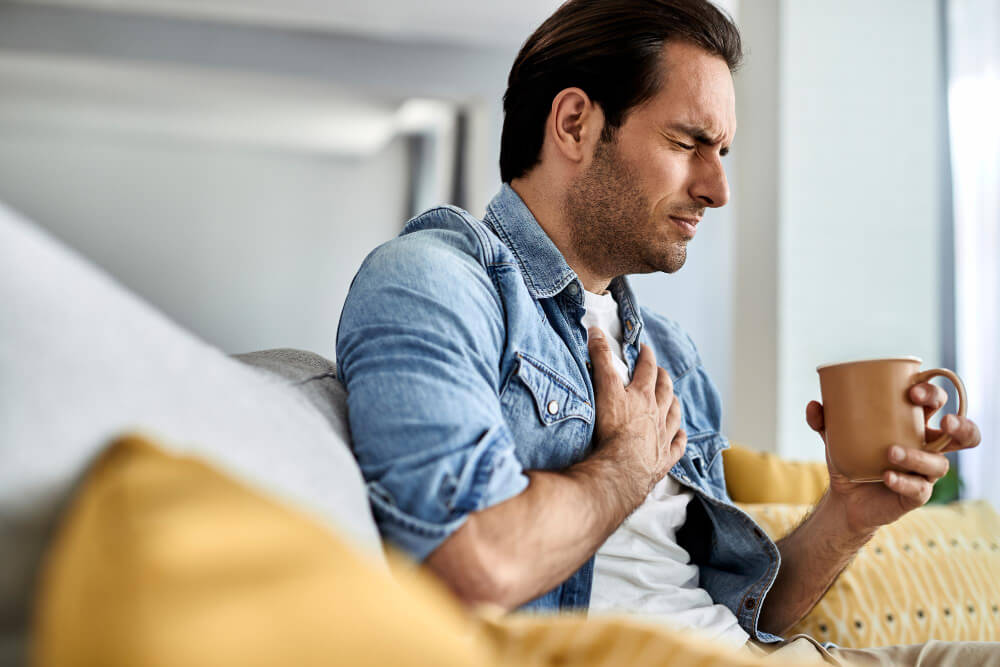
Although a silent heart attack doesn’t cause the typical chest pain and shortness of breath associated with a traditional heart attack, there are still some symptoms that may occur. These can include:
- Mild discomfort in the chest, arms, neck, jaw, or back
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
These symptoms may be mild and can often be mistaken for other conditions. As a result, many people may not seek medical attention until the damage has already been done.
Risk Factors
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of having a silent heart attack. These include:
- Age: The risk of a silent heart attack increases with age, especially after age 65.
- Gender: Men are more likely to have a silent heart attack than women.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of having a silent heart attack.
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the arteries and increase the risk of a silent heart attack.
- High cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause plaque buildup in the arteries, which can lead to a heart attack.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of a heart attack.
- Family history: If you have a family history of heart disease, you may be at a higher risk of having a silent heart attack.
Prevention
There are several things you can do to reduce your risk of having a silent heart attack. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet low in saturated fat, trans fat, and cholesterol can help keep your heart healthy.
- Exercising regularly: Regular physical activity can help keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk of heart disease.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of heart disease.
- Managing stress: Stress can contribute to heart disease, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise or meditation.
- Quitting smoking: If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your heart health.
- Getting regular checkups: Regular checkups with your doctor can help detect any potential heart problems early on.

Treatment
If you have a silent heart attack, treatment may include medications such as aspirin or nitroglycerin to help improve blood flow to the heart. In some cases, a procedure called angioplasty may be performed to open up blocked arteries. Lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can also help improve heart health and prevent future heart problems. Also, contact a nearby cardiologist doctor.
Conclusion
A silent heart attack is a serious condition that can go unnoticed if you don’t know what to look for. It’s important to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with this type of heart attack so that you can take steps to reduce your risk. By making healthy lifestyle choices and getting regular checkups with your doctor, you can help keep your heart healthy and prevent serious complications from a silent heart.
Also read: Heart Failure Symptoms: Understanding the Signs and Seeking Treatment